Surgical Simulation with Virtual Reality: Reducing Errors in Invasive Procedures
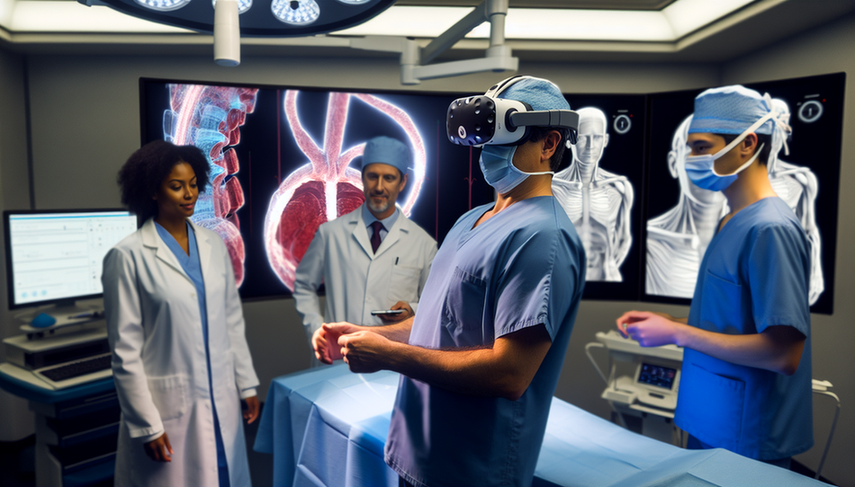
Virtual reality (VR) has emerged as a revolutionary tool in the field of medicine, particularly in the realm of invasive procedures. The ability to simulate complex surgical environments allows surgeons to practice and refine their skills without risk to patients. This technological advancement not only enhances surgical proficiency but also significantly contributes to error reduction during actual procedures.
Diving Deeper into the Use of Virtual Reality in Surgery
The use of VR in surgical training has proven to be highly effective. A recent study on an immersive virtual reality environment in orthopaedics highlights how this technology improves surgical skills and reduces errors, providing a realistic simulation environment that facilitates motor learning and functional recovery for patients. Additionally, VR offers a non-invasive and drug-free alternative for pain management.
In the field of laparoscopic surgery, VR has shown to be a valuable tool for training surgeons in training. Studies have demonstrated that training with VR simulators can significantly reduce operation time and improve operational performance compared to traditional training. This translates into a lower error rate and greater efficiency in the operating room.
The transfer of technical skills acquired in VR simulators to the operating room environment has been validated in randomized controlled studies. Residents who received VR training showed a significant improvement in their surgical performance, with fewer errors and faster dissection times compared to those who did not receive such training.
Conclusions
The integration of virtual reality in surgical training represents a significant advancement towards improving patient safety and operational efficiency. By allowing surgeons to practice in a controlled and simulated environment, VR not only enhances technical skills but also reduces the likelihood of errors during invasive procedures. As technology continues to advance, we are likely to see even greater adoption of these tools in daily clinical practice, benefiting both healthcare professionals and patients.
Referencias
- [1] Immersive virtual reality in orthopaedics-a narrative review.
- [2] Virtual reality training for surgical trainees in laparoscopic surgery.
- [3] Virtual reality training improves operating room performance: results of a randomized, double-blinded study.
Created 24/1/2025
